Article mis à jour le10 janvier 2026par l’équipe médicale et paramédicale du site|Publié le29 décembre 2020
Sources de l’article
- Yu C, Wang T, Gao Y, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci 2024; 13: 687-698.
- Sadafi S, et al. Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol 2024; 24: 43-.
- Ahmed HAA, et al. Psychological factors, lifestyle habits, and their association with gastroesophageal reflux disease among university students . Medicine (Baltimore) 2024; 103: e4321.
- Silva MTB, et al. Editorial: Exercise physiology and gastrointestinal disorders . Front Sports Active Living 2024; 6: 1404388.
- Gaskell SK, et al. Impact of exercise duration on gastrointestinal function and gastric slow-wave activity . J Appl Physiol 2023.
- DA Carlson, I Hirano. Reflux While Running: Something to Belch About. Am J Gastroenterol 2016 Jul.
- Herregods T, Van Hoeij F,Oors J, Bredenoord A, Smout A. Effect of Running on Gastroesophageal Reflux and Reflux Mechanisms. – The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 0.1038/ajg. 2016.122.
- Festi D ,Scaioli E, Baldi F et al. Body weight, lifestyle, dietary habits and gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15: 1690–701.
- Jozkow P,Wasko-Czopnik D, Dunajska K et al. The relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and the level of physical activity. Swiss Med Wkly 2007; 137: 465–70.
- Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA et al. Epidemiology of gastro-oesopha-geal reflux disease: a systematic review.Gut 2005; 54: 710–7.2.
- Ravi N, Stuart RC, Byrne PJ et al. Effect of physical exercise on esophageal motility in patients with esophageal disease. Dis Esophagus 2005; 18 : 374–7.
- Parmelee-Peters K, Moeller JL. Gastroesophageal reflux in athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep 2004; 3: 107–11.
- Pan do li no JE, Bianchi LK,Lee TJ et al. Esophagogastric junction morpho-logy predicts susceptibility to exercise-induced reflux. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99:1430–6.
- Collings KL, Pierce Pratt F,Rodriguez-Stanley S et al. Esophageal reflux in conditioned runners, cyclists, and weightlifters. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2003; 35: 730–5.


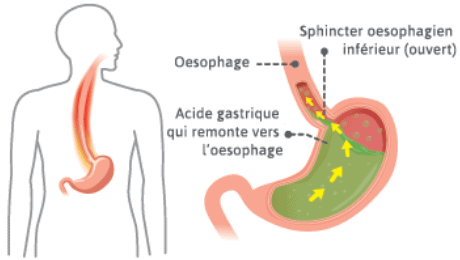
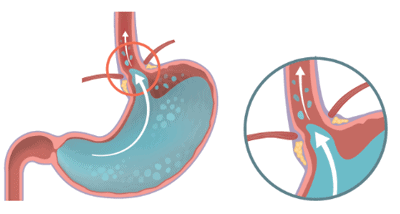
 Certains sports augmentent fortement la pression intra-abdominale, créent des secousses importantes ou demandent des efforts prolongés à haute intensité. Ces conditions favorisent l’apparition de reflux gastrique pendant ou après le sport.
Certains sports augmentent fortement la pression intra-abdominale, créent des secousses importantes ou demandent des efforts prolongés à haute intensité. Ces conditions favorisent l’apparition de reflux gastrique pendant ou après le sport.