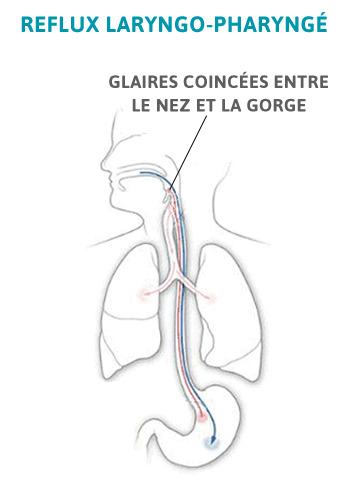
Article mis à jour le7 novembre 2025/Publié le14 novembre 2024
Source de l’article
- Kalamkas Sagandykova, Nataliya Papulova, Talapbek Azhenov, Aliya Darbekova, Bayan Aigozhina, Jerome R Lechien. Endoscopic Features of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug.
- Na Cui, Ting Dai, Yang Liu, Ya-Yu Wang, Jia-Yu Lin, et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: Updated examination of mechanisms, pathophysiology, treatment, and association with gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr.
- Lechien JR, Saussez S, Schindler A, Karkos P, et al. Symptoms and Signs Outcomes of Laryngopharyngeal reflux Treatment: A critical Systematic review and Meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2019 May.
- Lechien JR, Bobin F, Muls V, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux in laryngopharyngeal reflux patients: Clinical features and therapeutic response. Laryngoscope. 2019.
- Wang AM, Wang G, Huang N, Zheng YY, Yang F, Qiu X, Chen XM. Association between laryngopharyngeal reflux disease and autonomic nerve dysfunction. Eur Arch 20 Otorhinolaryngol. 2019.
- Zalvan CH, Hu S, Greenberg B, Geliebter J. A Comparison of Alkaline Water and Mediterranean Diet vs Proton Pump Inhibition for Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017.
- Javorkova N, Varechova S, Pecova R, et al. Acidification of the oesophagus acutely increases the cough sensitivity in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux and chronic cough. Neurogastroenterology and Motility. 2008
- Johnston N, Dettmar PW, Bishwokarma B, Lively MO, Koufman JA. Activity/stability of human pepsin: implications for reflux attributed laryngeal disease. Laryngoscope. 2007.
- Gill GA, Johnston N, Buda A, et al. Laryngeal epithelial defenses against laryngopharyngeal reflux: investigations of E-cadherin, carbonic anhydrase isoenzyme III, and pepsin. Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology I. 2005.
- Sasaki CT, Marotta J, Chow J, Hundal J, Eisen RN. Bile-induced laryngitis: is there a basis in evidence? Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology. 2005.
- Adhami T, Goldblum JR, Richter JE, Vaezi MF. The role of gastric and duodenal agents in laryngeal injury: an experimental canine model. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2004.
- Morice AH. Epidemiology of cough. Pulmonary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2002.
- Irwin RS, French CL, Curley FJ, Zawacki JK, Bennett FM. Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux: clinical, diagnostic, and pathogenetic aspects. Chest. 1993.
- Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury. Laryngoscope. 1991.